What is curl?
URL syntax and their use in curl Specifications. The official 'URL syntax' is primarily defined in these two different specifications: RFC 3986 (although URL is called 'URI' in there) The WHATWG URL Specification; RFC 3986 is the earlier one, and curl has always tried to adhere to. The presence of user name and password in the URL is completely optional. Curl also allows that information to be provide with normal command-line options, outside of the URL. Host name or address The host name part of the URL is, of course, simply a name that can be resolved to an numerical IP address, or the numerical address itself.
cURL, often just “curl,” is a free command line tool. It uses URL syntax to transfer data to and from servers. curl is a widely used because of its ability to be flexible and complete complex tasks. For example, you can use curl for things like user authentication, HTTP post, SSL connections, proxy support, FTP uploads, and more! You can also do simple things with curl, such as download web pages and web images. Read on to find out if you should use curl, and if so, common use cases that will get you started.
Should You Use curl?
Whether or not you should use curl depends on your goals. For simpler goals, you may want to check out wget. curl is great for complex operations since it is scriptable and versatile. However, wget is easier to understand and more user-friendly, so we recommend using it for simpler tasks.
curl Protocols
curl has many different supported protocols. However, curl will use HTTP protocol by default if no protocol is provided. For example, if you run the following example, it would download the homepage of example.com.
You can call a specific protocol by prefacing the URL with the protocol name.
The example above uses the HTTP protocol. If you want to use a different protocol, switch HTTP out for another. For example, if you wanted to use the FTP protocol, it would look like this:
curl will also try different protocols if the default protocol doesn’t work. If you give it hints, curl can guess what protocol you want to use.
For example, if you wrote the following command, curl would be able to intelligently guess that you wanted to use the FTP:// protocol.
Here’s a list of curl supported protocols:
| DICT | FILE | FTP |
| FTPS | GOPHER | HTTP |
| HTTPS | IMAP | IMAPS |
| LDAP | POP3 | RTMP |
| RTSP | SCP | SFTP |
| SMB | SMBS | TELNET |
| TFTP |
Basics: How to Use curl
We touched on how to use curl protocols briefly, which may have given you some idea on how to use curl. At its most basic, curl tends to follow this format:
You can find a list of possible options on the curl documentation site. Options will direct curl to perform certain actions on the URL listed. The URL gives curl the path to the server it should perform the action on. You can list one URL, several URLs, or parts of a URL, depending on the nature of your option.
Listing more than one URL:
Listing different parts of a URL:
Saving URL to File
You can also use curl to save the content of the URL to a file. There are two different methods for doing this: the -o and the -O method. When you use the -o option, you can add a filename that the URL will be saved as. A command using the -o option would look something like this:
Notice that the filename the URL will be saved in is placed between the -o option and the URL.
The -O method allows you to save the file under the same name as the URL. When using the -O option, no filename is required between the option and the URL. Instead, the command will look something like this:
Continuing a Download
If your download is stopped, you can restart it again with a simple curl command. It’s very simple, all you need to do is rewrite the command with the addition of the -C option.
If you were saving a URL, but the process was halted, you can restart the process by typing in the following:
This would pick the process back up where it had halted before.
Specify Time Frame for Download
Download files before or after a certain time by using curl. To do this, use the -z option, then list the date.
The -z option will search for files after the designated time frame by default. To search for files beforethe time listed, you can add a dash in front of the date. It will look like this:
Showing curl Output
curl will often not show any output after you have executed a command, which can be frustrating if you are trying to learn the ropes. The good news? curl has an option that allows you to view curl as it works.
You just need to add a -v to the command to view curl’s internal runnings as it executes. This can be especially helpful when you receive a response from curl that you didn’t anticipate. By viewing curl with -v, you can see what curl is actually doing behind the scenes. Simply run the command to turn it on.
Here’s an example of what a command with the -v option would look like:
If you get tired of seeing the internal workings of curl, you can also turn this feature off by using the –no-verbose option. Just switch the -v option out for –no-verbose, and curl will stop showing the internal process.
curl in Review
curl is a powerful, flexible tool. The commands touched on here were only the tip of the iceberg – curl has the ability to work with a multitude of protocols and, while we only touched on HTTP-specific options. Stay tuned for more blog posts about curl in the future. You can be notified as soon as a new blog post comes out.
If you like the idea of curl, but think it might be too complex for you, check out our article on using wget.
cURL is a software package which consists of command line tool and a library for transferring data using URL syntax.
cURL supports various protocols like, DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, Gopher, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, SMTPS, Telnet and TFTP.
This article provides 15 practical cURL usage examples.
1. Download a Single File
The following command will get the content of the URL and display it in the STDOUT (i.e on your terminal).
To store the output in a file, you an redirect it as shown below. This will also display some additional download statistics.
2. Save the cURL Output to a file
We can save the result of the curl command to a file by using -o/-O options.
- -o (lowercase o) the result will be saved in the filename provided in the command line
- -O (uppercase O) the filename in the URL will be taken and it will be used as the filename to store the result
Now the page gettext.html will be saved in the file named ‘mygettext.html’. You can also note that when running curl with -o option, it displays the progress meter for the download as follows.
When you use curl -O (uppercase O), it will save the content in the file named ‘gettext.html’ itself in the local machine.
Note: When curl has to write the data to the terminal, it disables the Progress Meter, to avoid confusion in printing. We can use ‘>’|’-o’|’-O’ options to move the result to a file.
Similar to cURL, you can also use wget to download files. Refer to wget examples to understand how to use wget effectively.
3. Fetch Multiple Files at a time
We can download multiple files in a single shot by specifying the URLs on the command line.
Syntax:
The below command will download both index.html and gettext.html and save it in the same name under the current directory.
Please note that when we download multiple files from a same sever as shown above, curl will try to re-use the connection.
4. Follow HTTP Location Headers with -L option
By default CURL doesn’t follow the HTTP Location headers. It is also termed as Redirects. When a requested web page is moved to another place, then an HTTP Location header will be sent as a Response and it will have where the actual web page is located.
For example, when someone types google.com in the browser from India, it will be automatically redirected to ‘google.co.in’. This is done based on the HTTP Location header as shown below.
The above output says that the requested document is moved to ‘http://www.google.co.in/’.
We can insists curl to follow the redirection using -L option, as shown below. Now it will download the google.co.in’s html source code.
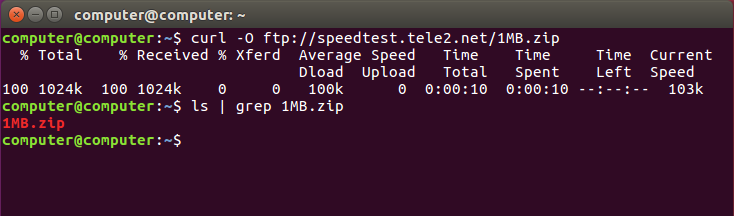
5. Continue/Resume a Previous Download
Using curl -C option, you can continue a download which was stopped already for some reason. This will be helpful when you download large files, and the download got interrupted.
If we say ‘-C -‘, then curl will find from where to start resuming the download. We can also give an offset ‘-C <offset>’. The given offset bytes will be skipped from the beginning for the source file.
Start a big download using curl, and press Ctrl-C to stop it in between the download.
Note: -# is used to display a progress bar instead of a progress meter.
Now the above download was stopped at 20.1%. Using “curl -C -“, we can continue the download from where it left off earlier. Now the download continues from 20.1%.
6. Limit the Rate of Data Transfer
You can limit the amount at which the data gets transferred using –limit-rate option. You can specify the maximum transfer rate as argument.
The above command is limiting the data transfer to 1000 Bytes/second. curl may use higher transfer rate for short span of time. But on an average, it will come around to 1000B/second.
The following was the progress meter for the above command. You can see that the current speed is near to the 1000 Bytes.
7. Download a file only if it is modified before/after the given time
We can get the files that are modified after a particular time using -z option in curl. This will work for both FTP & HTTP.
The above command will download the yy.html only if it is modified later than the given date and time
The above command will download the yy.html, if it is modified before than the given date and time.

Please refer ‘man curl_getdate’ for the various syntax supported for the date expression
8. Pass HTTP Authentication in cURL
Sometime, websites will require a username and password to view the content ( can be done with .htaccess file ). With the help of -u option, we can pass those credentials from cURL to the web server as shown below.
Note: By default curl uses Basic HTTP Authentication. We can specify other authentication method using –ntlm | –digest.
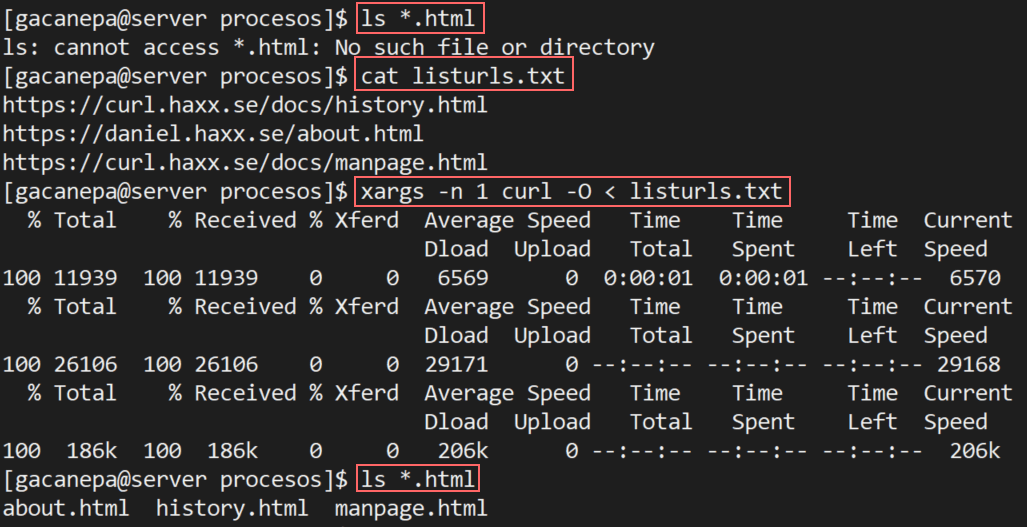
9. Download Files from FTP server
cURL can also be used to download files from FTP servers. If the given FTP path is a directory, by default it will list the files under the specific directory.
The above command will download the xss.php file from the ftp server and save it in the local directory.
Here, the given URL refers to a directory. So cURL will list all the files and directories under the given URL
If you are new to FTP/sFTP, refer ftp sftp tutorial for beginners.
10. List/Download using Ranges
cURL supports ranges to be given in the URL. When a range is given, files matching within the range will be downloaded. It will be helpful to download packages from the FTP mirror sites.
The above command will list out all the packages from a-z ranges in the terminal.
11. Upload Files to FTP Server
Curl can also be used to upload files to the FTP server with -T option.
The above command will upload the file named myfile.txt to the FTP server. You can also upload multiple files at a same time using the range operations.
Optionally we can use “.” to get the input from STDIN and transfer to the remote.
The above command will get the input from the user from Standard Input and save the contents in the ftp server under the name ‘myfile_1.txt’.
You can provide one ‘-T’ for each URL and the pair specifies what to upload where. Willem eprom programmer pcb50 downloadunbound.
12. More Information using Verbose and Trace Option
You can get to know what is happening using the -v option. -v option enable the verbose mode and it will print the details
The about command will output the following
If you need more detailed information then you can use the –trace option. The trace option will enable a full trace dump of all incoming/outgoing data to the given file
Curl Url Using Bad/illegal Format
This verbose and trace option will come in handy when curl fails due to some reason and we don’t know why.
13. Get Definition of a Word using DICT Protocol
You can use cURL to get the definition for a word with the help of DICT protocol. We need to pass a Dictionary Server URL to it.
The above command will list the meaning for bash as follows
Now you can see that it uses “The Collaborative International Dictionary of English”. There are many dictionaries are available. We can list all the dictionaries using
Now in-order to find the actual meaning of Bash in computer we can search for bash in “foldoc” dictionary as follows
Curl Url -v
The result will be,
For more details with regard to DICT please read RFC2229
14. Use Proxy to Download a File
We can specify cURL to use proxy to do the specific operation using -x option. We need to specify the host and port of the proxy.
15. Send Mail using SMTP Protocol
cURL can also be used to send mail using the SMTP protocol. You should specify the from-address, to-address, and the mailserver ip-address as shown below.
Curl Https Url
Once the above command is entered, it will wait for the user to provide the data to mail. Once you’ve composed your message, type . (period) as the last line, which will send the email immediately.
